Reminder: You may click on any slide image
for an enlarged view.
Tissue Presentation
- Strips of cells
- Rosette formation
- Feathering
- Crowding
- Stratification
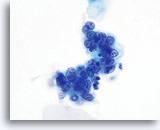
Adenocarcinoma in situ
A strip of endocervical cells exhibiting pseudostratification and finely vacuolated cytoplasm with indistinct cytoplasmic borders. Architecture is disrupted although cells are still attempting to maintain a glandular configuration. Note increased N/C ratio and the variable presence of nucleoli. Biopsy – AIS – 60x
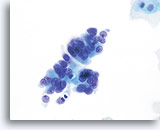
Adenocarcinoma in situ
Endocervical cells presenting in a pseudo-rosette formation and exhibiting “feathering” and nuclear elongation due to crowding. Biopsy – AIS – 60x
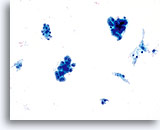
Adenocarcinoma in situ
Variably sized, crowded, hyperchromatic groups of cells are seen on screening power which warrant a closer inspection. 20x
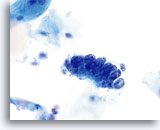
Adenocarcinoma in situ
Endocervical cells presenting in a strip with pronounced nuclear crowding. Biopsy – AIS – 60x
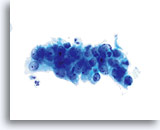
Adenocarcinoma in situ
This crowded, stratified group of glandular cells comes from a case of AIS. Note the basal nuclei piling up from the lower layer of the epithelium. 60x
Cytoplasm
- Scant
- Finely vacuolated
- Indistinct cytoplasmic borders
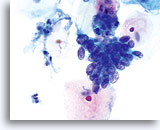
Adenocarcinoma in situ
AIS – 60x

Adenocarcinoma in situ
A strip of endocervical cells exhibiting pseudostratification and finely vacuolated cytoplasm with indistinct cytoplasmic borders. Architecture is disrupted although cells are still attempting to maintain a glandular configuration. Note increased N/C ratio and the variable presence of nucleoli. Biopsy – AIS – 60x
N/C
- Nucleus takes up 2/3 of the cytoplasm
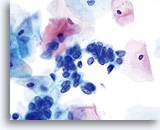
Adenocarcinoma in situ
High N/C ratios are evident in nuclei that take up at least 2/3 of the cytoplasm. Chromatin is coarse but evenly distributed and micronucleoli are present. Biopsy – AIS – 60x
Nucleus

Adenocarcinoma in situ
Endocervical cells presenting in a pseudo-rosette formation and exhibiting “feathering” and nuclear elongation due to crowding. Biopsy – AIS – 60x
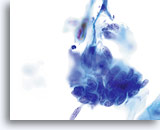
Adenocarcinoma in situ
Nuclear elongation is clearly evident in this group of atypical endocervical cells. Also noted is loss of nuclear polarity, loss of normal architecture, nuclear crowding, and “molding” of the nuclei. Note the flat nuclear membranes where they push up against each other (a sign of true crowding). Biopsy – AIS – 60x
Nuclear Membrane
- Smooth to markedly irregular
- Notching
- Thickened
Chromatin
- Coarse to finely granular
- Evenly distributed
- Hyperchromatic

Adenocarcinoma in situ
AIS – 60x
Nucleoli
- Indistinct to prominent
- Variably present
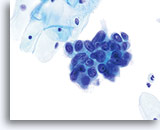
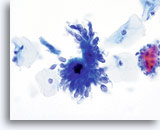
Adenocarcinoma in situ
Nucleoli can be indistinct to prominent. In this image, the nucleoli are prominent and present in a majority of the nuclei. Rapid fixation makes the presence of nucleoli another important piece of criteria in the diagnosis of AIS.
Biopsy – AIS – 60x
Look Alikes for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
Cell Type: Small cuboidal fallopian tube-type glandular
Tissue Presentation
- Crowded honeycomb presentation
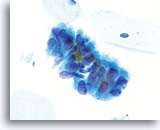
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
Tubal metaplasia can closely mimic AIS. However, on close inspection the abnormalities, ie: crowding, nuclear elongation, irregular nuclear membranes and abnormal tissue fragments are less severe. Locating cilia and/or terminal bars confirms benignancy. 60X
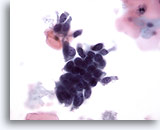
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
Crowded glandular cells have enlarged nuclei but a closer inspection reveals evenly distributed chromatin. 40x
Unique Features
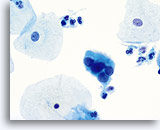
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
A strip of columnar cells with hyperchromatic, crowded nuclei. Close observation reveals distinct cytoplasmic vacuoles and cilia possibly representing tubal metaplasia. 60X
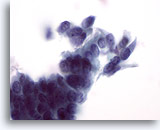
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
In this higher power view of the first photograph (20x) a distinct row of cilia is evident. 60x
Cell Type: Endometrial
Tissue Presentation
- Honeycomb presentation with overlapping nuclei, often in large sheets
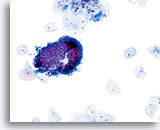
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
A fragment of cells from the lower uterine segment, which has folded over itself causing a three dimensional appearance. 20X
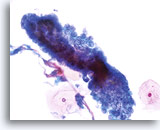
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
Lower uterine segment – 40X
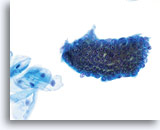
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
Lower uterine segment may have prominent nucleoli. 40X
Unique Features
- Very small cells with scant cytoplasm and uniform appearance
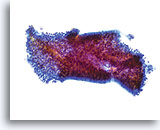
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
This tissue fragment of lower uterine segment is composed of small, cuboidal cells with uniform nuclei and bland chromatin. At low power the cells appear crowded; however on closer inspection they are simply tightly packed. The cohesiveness and uniformity of such fragments at low power are the keys to diagnosis. A stromal component is usually present as well and is an aid in diagnosis. 20x
Tissue Presentation
- Definitive squamous component
- Sheets of poorly defined epithelium
- Foamy cytoplasm and no definitive glandular differentiation
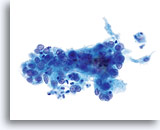
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
HSIL involving the gland space – 40x
Cytoplasm
- Finely vacuolated
- No discrete vacuoles
- Ill-defined cytoplasm at group edges (frayed appearance)
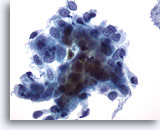
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
HSIL in glands – Finely vacuolated cytoplasm, with ill defined borders, creates a frayed appearance. 40x
Nucleus
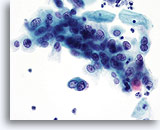
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
HSIL – Nuclei show variability in shape (round to oval) and size. 40x
Nuclear Membrane
- Smooth to irregular, (bites and divots)
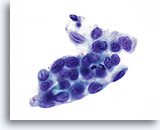
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
HSIL – Nuclei show irregularities within the membrane creating bites and divots. 60x
Chromatin
- Finely granular
- Evenly distributed
- Greater depth of focus
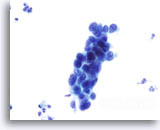
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
HSIL in glands – Variable chromatin, usually finely granular and evenly distributed with a depth of focus. 40x
Nucleoli
- Absent to occasional, small
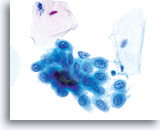
Look Alike for Endocervical Adenocarcinoma in situ
HSIL – Nucleoli generally inconspicuous or absent. Nucleoli may be present when there is a concurrent inflammatory/reactive process or when gland neck involvement is present. 60x