Urinary Tract Cytology – Normal Elements
NORMAL ELEMENTS
Reminder: You may click on any slide image
for an enlarged view.
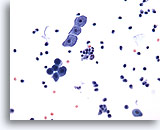
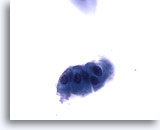
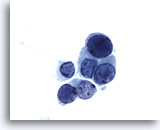
Figure 1
Voided urine, negative
Voided urine is the most readily obtainable urinary specimen.
20x
Voided urine, negative
Voided urine is the most readily obtainable urinary specimen.
20x
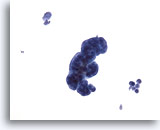
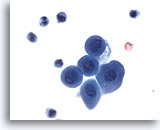
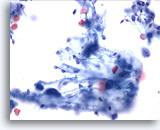
Figure 2
Catheterized urine, negative
Catheterized urine specimens often contain clusters of cells, removed during instrumentation. 20x
Catheterized urine, negative
Catheterized urine specimens often contain clusters of cells, removed during instrumentation. 20x
Figure 2
Catheterized urine, negative
Catheterized urine specimens often contain clusters of cells, removed during instrumentation.
20x
Catheterized urine, negative
Catheterized urine specimens often contain clusters of cells, removed during instrumentation.
20x
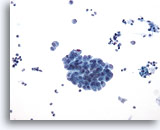
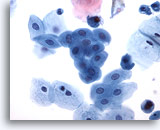
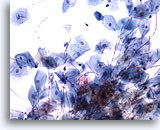
Figure 3
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Washings involve lavage with 50 mls of saline before bladder manipulation and usually result in richly cellular specimens. 20x
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Washings involve lavage with 50 mls of saline before bladder manipulation and usually result in richly cellular specimens. 20x
Figure 3
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Washings involve lavage with 50 mls of saline before bladder manipulation and usually result in richly cellular specimens.
20x
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Washings involve lavage with 50 mls of saline before bladder manipulation and usually result in richly cellular specimens.
20x

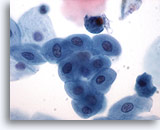
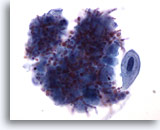
Figure 4
Intestinal conduit urine, negative
Washings from a loop urine contain benign glandular cells. 40x
Intestinal conduit urine, negative
Washings from a loop urine contain benign glandular cells. 40x
Figure 4
Intestinal conduit urine, negative
Washings from a loop urine contain benign glandular cells.
40x
Intestinal conduit urine, negative
Washings from a loop urine contain benign glandular cells.
40x
Figure 5
Voided urine, negative
Parabasal-like urothelial cells look metaplastic.
60x
Voided urine, negative
Parabasal-like urothelial cells look metaplastic.
60x
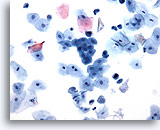
Figure 6
Urine, negative
Urothelial cells may be round and mononuclear as pictured in figures 6-8. 20x
Urine, negative
Urothelial cells may be round and mononuclear as pictured in figures 6-8. 20x
Figure 6
Urine, negative
Urothelial cells may be round and mononuclear as pictured in figures 6-8.
20x
Urine, negative
Urothelial cells may be round and mononuclear as pictured in figures 6-8.
20x
Figure 7
Urine, negative
40x
Urine, negative
40x
Figure 8
Urine, negative
60x
Urine, negative
60x
Figure 9
Urine, negative
Normal urothelial cells may appear columnar.
60x
Urine, negative
Normal urothelial cells may appear columnar.
60x
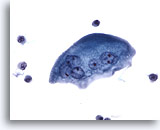
Figure 10
Urine, negative
Umbrella cells are large and usually multinucleated. The cytoplasm of this umbrella cell is finely vacuolated. 40x
Urine, negative
Umbrella cells are large and usually multinucleated. The cytoplasm of this umbrella cell is finely vacuolated. 40x
Figure 10
Urine, negative
Umbrella cells are large and usually multinucleated. The cytoplasm of this umbrella cell is finely vacuolated.
40x
Urine, negative
Umbrella cells are large and usually multinucleated. The cytoplasm of this umbrella cell is finely vacuolated.
40x
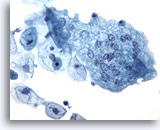
Figure 11
Catheterized urine, negative
Nuclei of umbrella cells are round to ovoid with finely granular chromatin and small nucleoli. 40x
Catheterized urine, negative
Nuclei of umbrella cells are round to ovoid with finely granular chromatin and small nucleoli. 40x
Figure 11
Catheterized urine, negative
Nuclei of umbrella cells are round to ovoid with finely granular chromatin and small nucleoli.
40x
Catheterized urine, negative
Nuclei of umbrella cells are round to ovoid with finely granular chromatin and small nucleoli.
40x
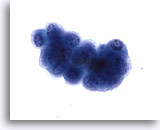
Figure 12
Voided urine, atypical
Voided urine samples may contain cell clusters and hence be labeled “atypical.” Approximately 20% of these samples are normal. 60x
Voided urine, atypical
Voided urine samples may contain cell clusters and hence be labeled “atypical.” Approximately 20% of these samples are normal. 60x
Figure 12
Voided urine, atypical
Voided urine samples may contain cell clusters and hence be labeled “atypical”. Approximately 20% of these samples are normal.
60x
Voided urine, atypical
Voided urine samples may contain cell clusters and hence be labeled “atypical”. Approximately 20% of these samples are normal.
60x
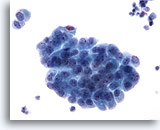
Figure 13
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Benign cell clusters in washings show nuclei that can be either pale or hyperchromatic and may contain one or more nucleoli. 40x
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Benign cell clusters in washings show nuclei that can be either pale or hyperchromatic and may contain one or more nucleoli. 40x
Figure 13
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Benign cell clusters in washings show nuclei that can be either pale or hyperchromatic and may contain one or more nucleoli.
40x
Renal pelvis washing, negative
Benign cell clusters in washings show nuclei that can be either pale or hyperchromatic and may contain one or more nucleoli.
40x
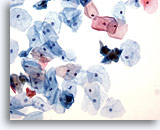
Figure 14
Urine, negative
Squamous cells may be present as contaminants from external genitalia or as cells shed from the trigone. 20x
Urine, negative
Squamous cells may be present as contaminants from external genitalia or as cells shed from the trigone. 20x
Figure 14
Urine, negative
Squamous cells may be present as contaminants from external genitalia or as cells shed from the trigone.
20x
Urine, negative
Squamous cells may be present as contaminants from external genitalia or as cells shed from the trigone.
20x
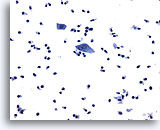
Figure 15
Urine, negative
Presence of inflammation in urinary samples may indicate trauma, infection or tumor. 20x
Urine, negative
Presence of inflammation in urinary samples may indicate trauma, infection or tumor. 20x
Figure 15
Urine, negative
Presence of inflammation in urinary samples may indicate trauma, infection or tumor.
20x
Urine, negative
Presence of inflammation in urinary samples may indicate trauma, infection or tumor.
20x
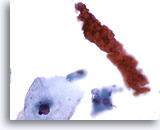
Figure 16
Urine, negative
Benign urinary samples are normally free of blood. Red blood cell casts may indicate bleeding in the kidney. 60x
Urine, negative
Benign urinary samples are normally free of blood. Red blood cell casts may indicate bleeding in the kidney. 60x
Figure 16
Urine, negative
Benign urinary samples are normally free of blood. Red blood cell casts may indicate bleeding in the kidney.
60x
Urine, negative
Benign urinary samples are normally free of blood. Red blood cell casts may indicate bleeding in the kidney.
60x
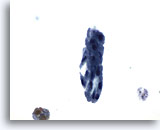
Figure 17
Urine, negative
Renal tubular cells are small and columnar and may appear singly or in renal tubular cell casts as pictured. 60x
Urine, negative
Renal tubular cells are small and columnar and may appear singly or in renal tubular cell casts as pictured. 60x
Figure 17
Urine, negative
Renal tubular cells are small and columnar and may appear singly or in renal tubular cell casts as pictured.
60x
Urine, negative
Renal tubular cells are small and columnar and may appear singly or in renal tubular cell casts as pictured.
60x
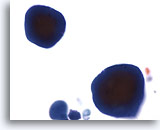
Figure 18
Urine, negative
Copora amylacea are laminated non-calcified bodies originating in the prostate gland. 60x
Urine, negative
Copora amylacea are laminated non-calcified bodies originating in the prostate gland. 60x
Figure 18
Urine, negative
Copora amylacea are laminated non-calcified bodies originating in the prostate gland.
60x
Urine, negative
Copora amylacea are laminated non-calcified bodies originating in the prostate gland.
60x
Figure 19
Urine, negative
Sperm may also appear in urine.
60x
Urine, negative
Sperm may also appear in urine.
60x
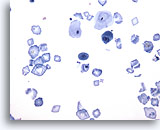
Figure 20
Urine, negative
Crystals may be present in urine, but are routinely analyzed during urinalysis. 20x
Urine, negative
Crystals may be present in urine, but are routinely analyzed during urinalysis. 20x
Figure 20
Urine, negative
Crystals may be present in urine, but are routinely analyzed during urinalysis.
20x
Urine, negative
Crystals may be present in urine, but are routinely analyzed during urinalysis.
20x
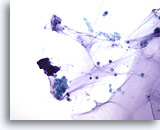
Figure 21
Ileal conduit urine, negative
Lubricant, cytoplasmic debris and glandular cells resembling macrophages make diagnosing malignancy challenging. 40x
Ileal conduit urine, negative
Lubricant, cytoplasmic debris and glandular cells resembling macrophages make diagnosing malignancy challenging. 40x
Figure 21
Ileal conduit urine, negative
Lubricant, cytoplasmic debris and glandular cells resembling macrophages make diagnosing malignancy challenging.
40x
Ileal conduit urine, negative
Lubricant, cytoplasmic debris and glandular cells resembling macrophages make diagnosing malignancy challenging.
40x
Figure 22
Urine, negative
Candida is the most common fungal infection of the urinary tract.
20x
Urine, negative
Candida is the most common fungal infection of the urinary tract.
20x
Figure 23
Voided urine, negative
Candida is seen as pseudo-hyphae or spores.
60x
Voided urine, negative
Candida is seen as pseudo-hyphae or spores.
60x
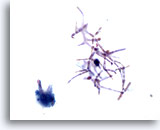
Figure 24
Voided urine, negative
Candida may occur as a contaminant from the vagina in female patients. 60x
Voided urine, negative
Candida may occur as a contaminant from the vagina in female patients. 60x
Figure 24
Voided urine, negative
Candida may occur as a contaminant from the vagina in female patients.
60x
Voided urine, negative
Candida may occur as a contaminant from the vagina in female patients.
60x
Figure 25
Urine, negative
Cells infected with polyoma virus vary in size.
60x
Urine, negative
Cells infected with polyoma virus vary in size.
60x
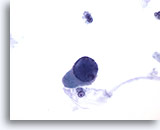
Figure 26
Urine, negative
“Decoy cells” caused by polyoma virus mimic cancer and have basophilic opaque intranuclear inclusions. 60x
Urine, negative
“Decoy cells” caused by polyoma virus mimic cancer and have basophilic opaque intranuclear inclusions. 60x
Figure 26
Urine, negative
“Decoy cells” caused by polyoma virus mimic cancer and have basophilic opaque intranuclear inclusions.
60x
Urine, negative
“Decoy cells” caused by polyoma virus mimic cancer and have basophilic opaque intranuclear inclusions.
60x
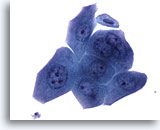
Figure 27
Urine, atypical
The presence of stones can result in nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia, prominent nucleoli and occasional mitosis. 60x
Urine, atypical
The presence of stones can result in nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia, prominent nucleoli and occasional mitosis. 60x
Figure 27
Urine, atypical
The presence of stones can result in nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia, prominent nucleoli and occasional mitosis.
60x
Urine, atypical
The presence of stones can result in nuclear enlargement, hyperchromasia, prominent nucleoli and occasional mitosis.
60x
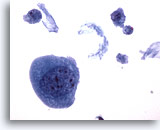
Figure 28
Urine, atypical
Sometimes the atypia from lithiasis is so severe that further workup to exclude malignancy is necessary. 40x
Urine, atypical
Sometimes the atypia from lithiasis is so severe that further workup to exclude malignancy is necessary. 40x
Figure 28
Urine, atypical
Sometimes the atypia from lithiasis is so severe that further workup to exclude malignancy is necessary.
40x
Urine, atypical
Sometimes the atypia from lithiasis is so severe that further workup to exclude malignancy is necessary.
40x
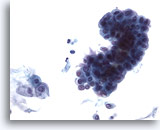
Figure 29
Urine, suspicious
The presence of stones can result in large clusters and papillary fragments with marked variation in shape and size of the urothelial cells. 40x
Urine, suspicious
The presence of stones can result in large clusters and papillary fragments with marked variation in shape and size of the urothelial cells. 40x
Figure 29
Urine, suspicious
The presence of stones can result in large clusters and papillary fragments with marked variation in shape and size of the urothelial cells.
40x
Urine, suspicious
The presence of stones can result in large clusters and papillary fragments with marked variation in shape and size of the urothelial cells.
40x
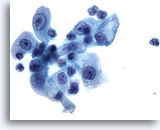
Figure 30
Urine, reactive
Cells have prominent nucleoli, nuclear enlargement and marked variation in size due to lithiasis. 60x
Urine, reactive
Cells have prominent nucleoli, nuclear enlargement and marked variation in size due to lithiasis. 60x
Figure 30
Urine, reactive
Cells have prominent nucleoli, nuclear enlargement and marked variation in size due to lithiasis.
60x
Urine, reactive
Cells have prominent nucleoli, nuclear enlargement and marked variation in size due to lithiasis.
60x