Reminder: You may click on any slide image
for an enlarged view.
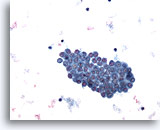
Figure 1
Pleural effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells 20X
Figure 1
Pleural effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells
20X
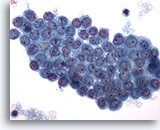
Figure 2
Pleural effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells 40X
Figure 2
Pleural effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells
40X
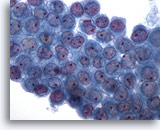
Figure 3
Pleural effusion: Benign mesothelial cells 60X
Figure 3
Pleural effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells
60X
Figures 1-3 – Pleural effusion: Benign mesothelial cells.
Sheets of benign mesothelial cells are often smaller than 12 cells, but may sometimes be composed of upwards of 50 cells. In these photomicrographs, the even dispersal of uniform cells, with regular nuclei, delicate nuclear membranes and small round nucleoli signal the benign nature of these cells.
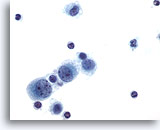
Figure 4
Pleural effusion: Reactive mesothelial cells. 60X
Figure 4
Pleural effusion:
Reactive mesothelial cells.
60X
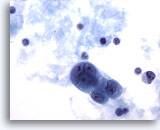
Figure 5
Pleural effusion: Reactive mesothelial cells. 60x
Figure 5
Pleural effusion:
Reactive mesothelial cells.
60x
Figs 4-5: Pleural effusion: Reactive mesothelial cells.
Under conditions of an inflammatory process, mesothelial cells are increased in number, can exhibit a wide range of sizes, and may be multinucleated. The keys to diagnosis involve (1) applying individual criteria of benignity and (2) establishing the presence of an uninterrupted continuum of sizes from small to very large. Note enlarged nuclei, small multiple nucleoli, and spaces between adjacent cells, so called “windows.” Inflammatory cells are present in the background.
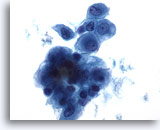
Figure 6
Peritoneal effusion: Reactive mesothelial cells. 60X
Figure 6
Peritoneal effusion:
Reactive mesothelial cells.
60X
Like pleural effusion, mesothelial cells in peritoneal effusions may exhibit a range of cell sizes. Mesothelial cells may be admixed with inflammatory cells and histiocytes.
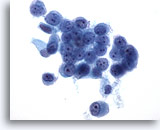
Figure 7
Peritoneal effusion: Benign. 60X
Figure 7
Peritoneal effusion:
Benign.
60X
This sheet of mesothelial cells exhibits moderate cohesion. Nuclei are uniform among cells in the group. Nuclear membranes are thin and delicate and nucleoli are small round and uniform.
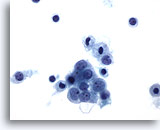
Figure 8
Peritoneal effusion: Reactive mesothelial cells. 60X
Figure 8
Peritoneal effusion:
Reactive mesothelial cells.
60X
Peritoneal effusion showing mild cellular anisocytosis as a reactive process.
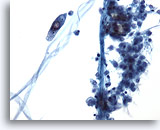
Figure 9
Pleural effusion: Arifacts. 20X
Figure 9
Pleural effusion:
Artifacts.
20X
Fibers from materials used for collection or specimen processing may be noted in body effusions from any site.
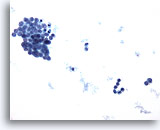
Figure 10
Pericardial effusion: Benign mesothelial cells. 20X
Figure 10
Pericardial effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells.
20X
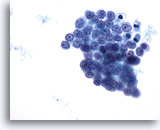
Figure 11
Pericardial effusion: Benign mesothelial cells. 40X
Figure 11
Pericardial effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells.
40X
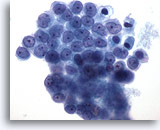
Figure 12
Pericardial effusion: Benign mesothelial cells. 60X
Figure 12
Pericardial effusion:
Benign mesothelial cells.
60X












